Build Yourself a GitLab Server with CI
Published:
GitLab in a docker is one of the minimal way to self-host a Git server with customized CI runners. Thanks to well-organized docker image offered by GitLab, this explore seems a pleasure rather than a nightmare.
Hey you! Fuchsia! Watch yourself!
Preliminary
The whole system is seperated to 2 parts:
- Main GitLab Framework, providing Git version control, web-based management and SSH service
- GitLab CI runner, working as an instance for carrying CI jobs
This exploration is completed on Ubuntu-20.04, with docker and other basic utils installed.
Setup GitLab Framework
Get IP Address as Host Address
First, get the IP address of your computer.
$ ifconfig
...
wlp1s0: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet 192.168.2.100 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.2.255
...
For example, my IP address is 192.168.2.100.
Set Environment Variable
$ echo GITLAB_HOME=/srv/gitlab
Start GitLab Docker
$ sudo docker run --detach \
--hostname 192.168.2.100 \
--publish 443:443 --publish 80:80 --publish 2222:22 \
--name gitlab \
--restart always \
--volume $GITLAB_HOME/config:/etc/gitlab \
--volume $GITLAB_HOME/logs:/var/log/gitlab \
--volume $GITLAB_HOME/data:/var/opt/gitlab \
gitlab/gitlab-ee:latest
About 3 minutes later, enter the hostname in your browser and check the familiar GitLab login page.
Login
The default username is root, and the password is generated randomly from the Docker process:
$ sudo docker exec -it gitlab grep 'Password:' /etc/gitlab/initial_root_password
Password: ...
And to manager the GitLab Website, enter your.customized.hostname/admin to reach the admin console.
Create an Example Repo and Trigger a CI
Create a blank repo and add a new file named .gitlab-ci.yml.
Enter the following:
build-job:
stage: build
script:
- echo "Hello, $GITLAB_USER_LOGIN!"
test-job1:
stage: test
script:
- echo "This job tests something"
test-job2:
stage: test
script:
- echo "This job tests something, but takes more time than test-job1."
- echo "After the echo commands complete, it runs the sleep command for 20 seconds"
- echo "which simulates a test that runs 20 seconds longer than test-job1"
- sleep 20
deploy-prod:
stage: deploy
script:
- echo "This job deploys something from the $CI_COMMIT_BRANCH branch."
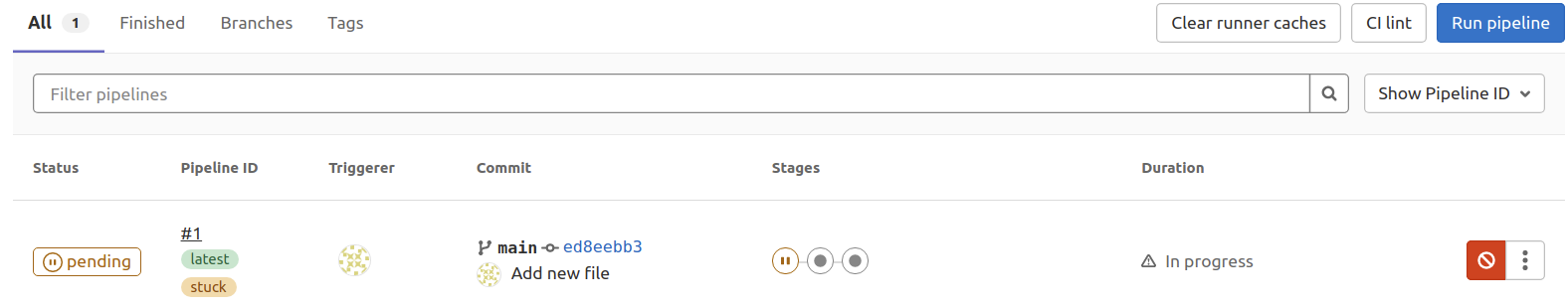
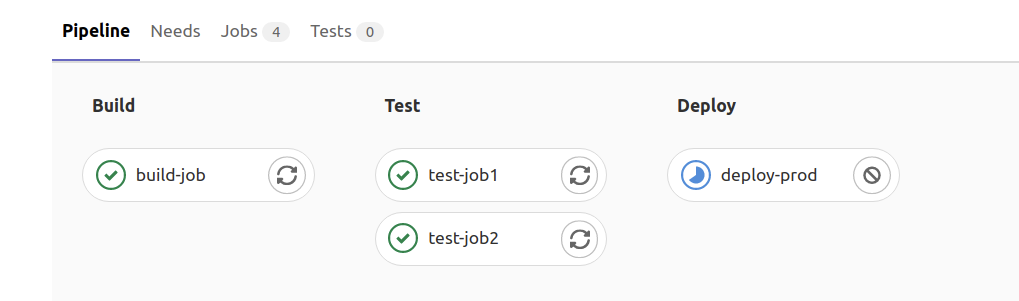
A CI is triggered. However, its status remains pending. Don’t worry, we have not created GitLab CI runner yet.
Create a GitLab CI Runner
First, create a GitLab CI runner throught docker engine.
$ docker run -d --name gitlab-runner --restart always \
-v /srv/gitlab-runner/config:/etc/gitlab-runner \
-v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock \
gitlab/gitlab-runner:latest
Then register the runner instance.
$ docker run --rm -it -v /srv/gitlab-runner/config:/etc/gitlab-runner gitlab/gitlab-runner register
Enter the information offered by GitLab CI settings panel.
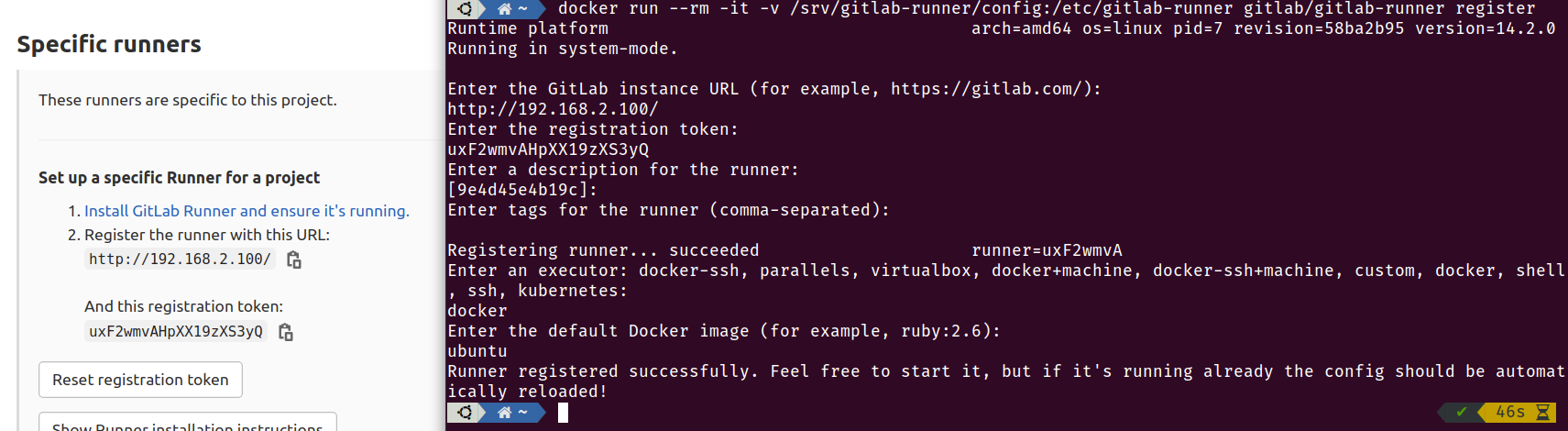
BOOM! CI Started!